In recent decades, increasing anthropogenic pressure on forest ecosystems—driven in part by the rising use of biomass for bioenergy, technical applications, and construction—has often led to the degradation of natural and semi-natural systems, especially in tropical regions. These trends are frequently associated with unsustainable and/or illegal exploitation of forest resources. The harvesting, processing, and transportation of wood and wood-based products have significant environmental, economic, and social impacts.
Over the last twenty years, political decision-makers, private companies, civil society organizations, and individual citizens have increasingly focused on the sustainable use of forest biomass. This has led to concrete actions and the implementation of effective tools aimed at preventing and mitigating such impacts. Forest certification has emerged as a key instrument to counteract the negative effects and threats to national and global forest resources by promoting practices based on careful planning and monitoring of wood biomass harvesting and management activities.
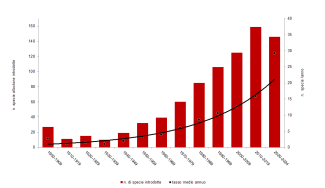
As of 31 December 2023, the forest area certified in Italy under the Programme for the Endorsement of Forest Certification (PEFC™) scheme amounted to 984,107 hectares (a 6% increase compared to 2022), while the area certified under the Forest Stewardship Council® (FSC®) scheme totalled 85,214 hectares (an increase of 4% over the previous year).