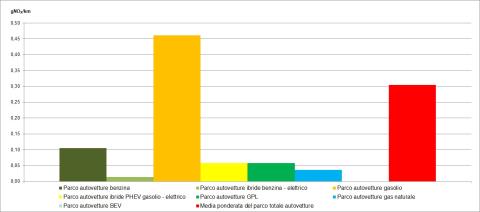
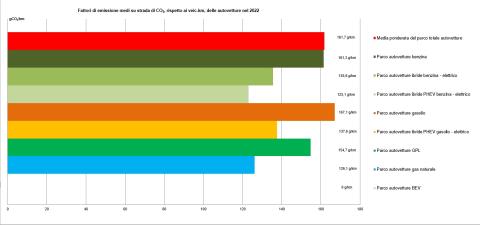
In Italy, the use of low environmental impact fuels is more widespread compared to other European countries.
This result has been facilitated by factors such as partial exemption from excise duties for these fuels and the allowance for vehicles powered by liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and natural gas to circulate in urban areas during traffic restriction periods.
Nevertheless, the use of low-impact fuels (of which biofuels account for 42,2%) remains limited. In 2023, they represented only 11% of total road fuel consumption: 6% from low-emission fossil fuels and 5% from biofuels, while gasoline and diesel still accounted for 89% of the total.