POTENTIAL EVAPOTRANSPIRATION
Data aggiornamento scheda:
The indicator provides, for each month of the year, the evaluation, by means of the Thornthwaite method, of the water height of per capitapiratospiration of monthly cumulated potential for the natural soil, expressed in mm, as follows to the surface of the national territory.
In 2024, the estimated value of the total potential annual subpostering on natural soil was 806,0 mm, deviating by +16% from the average value for the period 1951–2024, estimated at 695.4 mm.
GROUNDWATER RECHARGE
Data aggiornamento scheda:
The indicator provides, for each month and for the entire year, the evaluation of the monthly and annual cumulative water height, expressed in mm, in detail to the surface of the national territory, which infiltrates deep into the soil as a result of rainfall.
In 2024, the value of the annual total of the infiltration estimated at 226.8 mm, corresponding to 68.5 billion cubic meters, was slightly higher than the average of the period 1951, 2024 estimated at 216.1 mm, corresponding to 65.3 billion cubic meters.
PRECIPITATION
Data aggiornamento scheda:
The indicator provides the evaluation, expressed in mm, of the height of water, summarised to the surface of the national territory, which precipitates to the ground (both in liquid and solid form) for each month and for the entire year.
The indicator for 2024 shall be compared, for each month of the year, with the corresponding average values for the period 1951–2024 obtained by the same methodology. In 2024 the value of total annual rainfall in Italy was 1,055.5 mm (318.8 billion cubic meters), greater than 10% of the corresponding long-term average value (LTAA-Long-Term Annual Average) and about 8% compared to the annual average over the last thirty years of the climate 1991-2020.
Going down to the regional and district level, the situation is very diversified, with Northern Italy being affected in 2024 by quantities of precipitation higher than the long-term averages. On the other hand, the precipitation anomaly compared to the LTAA was negative in the Center and the South and the larger islands.
HYDROLOGICAL DROUGHT
Data aggiornamento scheda:
The 12-month Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) maps provide a nationwide and large-scale assessment of hydrological drought conditions, obtained using precipitation data collected and published by regional hydro-meteorological services and autonomous provinces and those of the suppressed National Hydrograph and Tire Service (SIMN, now merged into ISPRA) of the Department for National Technical Services. The 12-month aggregation timepiece chosen for the SPI assessment is the one that best describes the effects of drought (precipitation deficit) on the flow rate of rivers, recharging reservoirs and water availability in the aquifers.
In 2024, the 12-month SPI maps (SPI12) showed extreme and moderate drought conditions for the territories of central Italy and for the South and the major islands. The months from June to August 2024 were the most characterized by extreme drought conditions on the 12-month time scale (SPI12 –2.0), as a result of the precipitation deficit found in the second half of 2023 and then in 2024, particularly on southern Italy. The maximum extent reached by this condition was observed in June (16.1% of the Italian territory). From May 2024 until the end of the year, there was also an increase in areas characterized by severe or moderate drought on the 12-month time scale (–2.0 SPI12 –1.0). In this period, with the exception of October and December, the percentage of Italian territory subject to these conditions was always more than 20%, with a maximum in May (28.5%) and a minimum in September (21.6%).
The intensity and persistence of these conditions in 2024 had effects on the availability of water resources in different areas of Italy, resulting, consequently, in environmental and socio-economic impacts related to the use of water.
INTERNAL FLOW
Data aggiornamento scheda:
The internal flow indicator provides the annual estimate, expressed in mm, of the amount of renewable water resource that is naturally produced in a given territory due to the effect of precipitation falling in the same territory. The indicator is calculated for each year from 1951 to 2024.
In 2024 the value of the indicator at national level was 522.8 mm, corresponding to 157.9 billion cubic meters. The average value of the indicator in the national territory of the last thirty years of climate 1991–2020 is 440.9 mm, corresponding to a volume of 133.5 billion cubic meters, while the long-term average 1951–2024 (so-called LTAA-Long-Term Annual Average) is 457.5 mm, corresponding to 138.2 billion cubic meters.
2024 was characterized by a positive anomaly compared to the long-term estimate (+14.3%), as well as compared to the last thirty years of the climatological period (+18.3%). This positive anomaly is attributable to the high rainfall in the North, while in the territories of Central and Southern Italy and the major islands a persistent drought has been observed. However, at the national level, the availability of renewable water resources continues to show, from 1951 to the present, a statistically significant negative trend.
PERCENTAGE OF ITALIAN TERRITORY SUBJECT TO PRECIPITATION DEFICIT AND SURPLUS
Data aggiornamento scheda:
The indicator provides an assessment of the humidity conditions (surplus of precipitation compared to climatology) and drought (deficit of precipitation with respect to climatology) to which the national territory is subject, in terms of state and trend. For each month from 1952 to 2024, the percentage of Italian territory subject to a deficit and/or precipitation surplus is expressed through the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) relating to aggregate precipitation on the time scale of 3 and 12 months.
The 2024 was characterized, overall on a national scale, by a surplus of precipitation, to which the high volume of precipitation that poured into northern Italy contributed. Central Italy, South and the major islands have, on the other hand, continued to be characterized by a precipitation deficit.
This resulted in the highest percentage values of the national territory characterized by "extreme drought" (SPI -2.0) equal to 0.5% and 16.1%, respectively for cumulative precipitation over 3 months and the cumulative one over 12 months. The maximum percentage of national territory characterized by "severe or moderate drought" (?2.0 ? SPI ?1.0) was, instead, 24.1% on a time scale of 3 months and 28.5% on a 12-month time scale. On the other hand, on the 3-month time scale, the maximum values in the year of the percentage of the national territory characterized by "extreme humidity" (SPI ? 2.0) were 14.1%, while the maximum value relative to "severe or moderate humidity" (1.0 ? SPI ? 2.0) was equal to 42.1%. On a 12-month time scale, the percentage of the country affected by "extreme humidity" reached a maximum value of 20.8%, while the percentage with "severe or moderate humidity" reached a maximum of 28.4%.
ACTUAL EVAPOTRASPIRATION
Data aggiornamento scheda:
The indicator provides, for each month and for the entire year, the evaluation of the monthly and annual cumulative water height, expressed in mm, summarised to the surface of the national territory that is actually transferred to the atmosphere for evaporation phenomena from the liquid mirrors and the soil and perspiration of the vegetation and, therefore, does not contribute to the formation of renewable water resources.
In 2024, the estimated value of the total annual total real evapotranspiration was 540.3 mm, more than 9.5% at the average value for the period 1951–2024 estimated at 493.4 mm.
RUNOFF INDEX
Data aggiornamento scheda:
The indicator provides on an annual basis the assessment, expressed as a percentage, of the ratio between the annual volume of the runoff (surface preselling) and the annual volume of precipitation. This indicator aims to provide an assessment of the amount of water that is directly transformed into a surface runflow compared to total precipitation and to assess the trend over the long term, also in relation to the possible impact due to climate change. The annual values of the indicator shall also be compared with the corresponding average value calculated over the entire period 1951–2024.
In 2024, the value of the indicator was 26.1%, higher than the average value of 25.1% in the long term. This shows a trend reversal compared to 2023, in which there was a value of 23.7%, below the average. The comparison is even more marked with 2022, the year in which the indicator reached an all-time low of 18.5%.
STANDARDIZED HYDRO-CLIMATIC BALANCE
Data aggiornamento scheda:
The 12-month Standardized Precipitation-Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI) maps provide a nationwide and large-scale assessment of drought conditions and are obtained by analyzing the deviation of the hydro-climatic balance hydrological variable—defined as the difference between precipitation and potential evapotranspiration—from its reference climatology.
In 2024, the 12-month SPEI maps (SPEI12) highlight drought conditions, ranging from extreme to moderate, across central Italy, the South, and the major islands. The months from June to August 2024 were the most marked by extreme drought conditions on the 12-month timescale (SPEI12 ≤ –2.0), as a result of the precipitation deficit observed in the second half of 2023 and then in 2024, particularly in southern Italy, combined with the high temperatures that characterized all of 2024 (+1.33 °C anomaly in the average temperature compared to the 1991–2020 climatological mean).
The maximum extent of the hydro-climatic balance deficit was reached in June, with 33.5% of the Italian territory affected by extreme drought. Early in the year, the percentage of areas experiencing severe or moderate drought on the 12-month timescale (–2.0 < SPEI12 ≤ –1.0) was significant: 44.1% in January, 36.3% in February, and around 30% in March and April.
The intensity and persistence of these conditions in 2024 affected water resource availability in various areas of Italy, consequently causing environmental and socio-economic impacts related to water use.
WATER ABSTRACTION FOR CIVIL USE
Data aggiornamento scheda:
The indicator refers to 2022 and is drawn up on the basis of Istat data relating to the last “Nable Review for Civil Use” carried out in 2023 and published in 2024. The information is provided on a national, regional and by hydrographic district, divided in turn into removal from the surface and underground body water. The levy values are compared with those detected in the previous "Nail census for civil use" of 2020. Also in 2022, compared to the previous 2020 census, the water withdrawal for civil use in Italy has decreased slightly.
FLOWS
Data aggiornamento scheda:
The indicator provides an assessment of the trend of water volumes measured in bedside sections of some of the main Italian watercourses compared to the year and the previous decade. For 2021 it was possible to represent the data of scope for 6 sections of closure of as many waterways of national importance (Po, Arno, Adige, Bacchiglione, Serchio and Tiber). In 2021, the annual volumes drained in the measurement sections showed significant increases compared to 2020, with increases of between 6% and 25%, with the exception of the sections on the Adige and the Po.
AIR TEMPERATURE
Data aggiornamento scheda:
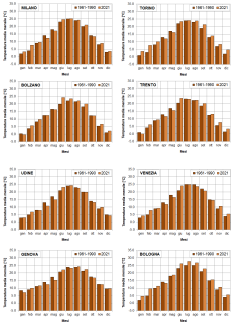
The indicator provides a representation of the trend of the average monthly temperatures recorded in the provincial capital city / region during 2021, compared with that of the average monthly temperatures calculated for the same locations over the thirty-year period 1961-1990. During 2021 there was a general increase in average monthly temperatures compared to the reference period, with exceedances of the reference values on average for 8 months and in particular in the summer and winter months. It is mainly the cities of the North where the temperature increases assume significant values in species in the months of February and December. It should be noted that in the months of April and October the temperature values, in most of the capitals, were on average lower than in the reference period.