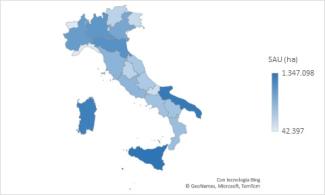
The indicator considers fertilisers used in agriculture, i.e. inputs primarily employed to support crop growth. It analyses their spatial and temporal distribution to provide an overall representation of environmental impact, based on the quantities and types of fertilisers placed on the market.
In 2023, more than 4.5 million tonnes of fertilisers were placed on the market.
Mineral fertilisers (including simple, compound, and those based on meso- and micronutrients) accounted for 40.7% of the total. This category has historically been the most sold, with the only exception in 2022, despite a long-term decline (2000–2023).
Organic fertilisers (including soil improvers and organic fertilisers) followed closely, representing 39.8% of total sales, with a long-term upward trend (2000–2023). The most sold subcategory was soil improvers, with over 1.2 million tonnes. Their sales volume has remained relatively stable in recent years and, for the second consecutive year, exceeded that of simple mineral fertilisers, which remain the dominant subcategory within mineral fertilisers (64.7%).