Aree
NATURA 2000 NETWORK
Data aggiornamento scheda:
Natura 2000 Network, established under the EU Habitats and Birds Directives (collectively known as the Nature Directives), comprises 2,649 sites in Italy. These cover a total terrestrial area of 5,845,489 hectares, representing 19.4% of the national territory, and a marine area of 2,338,693 hectares, corresponding to 6.5% of national jurisdictional waters (territorial waters and EEZs) (data updated to December 2024).
The Network is essential for implementing the Nature Directives, but it is also a key instrument for achieving the targets set by the European and National Biodiversity Strategies for 2030 (EBS2030 and NBS2030), which call for at least 30% of terrestrial and marine areas to be protected. In addition to the Natura 2000 sites, other protected areas—such as national and regional parks and other designated conservation zones—also contribute to these targets.
This report analyses the regional distribution of the Network both in absolute terms (hectares covered by sites within each region) and as a percentage of total regional area. Across Italian regions and autonomous provinces, the Network shows a heterogeneous distribution, with protected terrestrial and marine areas ranging from 12% (Emilia-Romagna) to 36% (Abruzzo) on land, and from less than 1% (Marche) to 31% (Apulia) at sea.
LAND CONSUMPTION IN PROTECTED AREAS
Data aggiornamento scheda:
The consumed soil within the terrestrial portion of Italian protected areas included in the Official List of Protected Areas (EUAP, 2010, updated with newly designated national protected areas established after 2010) is assessed with reference to National Parks, State and Regional Nature Reserves, Regional Nature Parks, and the other categories of national and regional protected natural areas.
As of 2024, 1.88% of the more than three million hectares of terrestrial EUAP areas (58,328 hectares) has been consumed, with the highest percentage in Campania (3.82%) and the lowest in the Alpine regions (Valle d’Aosta, Trentino-Alto Adige, and Friuli Venezia Giulia).
Between 2023 and 2024, Italian protected areas recorded an increase in soil consumption that remained below the national average (0.26 m² of change per hectare, compared to a national value of 2.60 m²/ha), amounting to a total of 80.96 hectares of newly consumed soil, more than 46% of which is concentrated in Abruzzo, Lazio, and Campania.
DISTRIBUTION OF ECOLOGICAL VALUE ACCORDING TO CARTA DELLA NATURA
Data aggiornamento scheda:
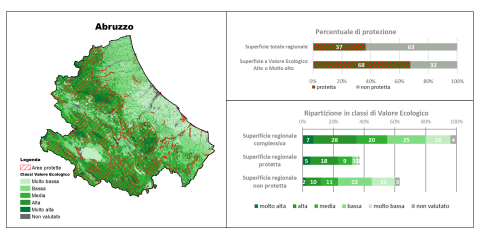
The indicator, based on data processed within the Carta della Natura project, shows the distribution of Ecological Value (VE) across 17 Italian regions, providing a representation categorized into different classes. Ecological Value is understood as a synonym for natural significance and is calculated—starting from the regional habitat maps—for each mapped polygon, excluding those referring to built environments and fully urbanized areas. This indicator offers an overview of the environmental mosaic within various regional contexts, highlighting high-value areas, including their protection status. The analysis presents the percentage of protected areas in each region and the composition of protected and unprotected zones in terms of Ecological Value. The protected areas system (EUAP areas, Natura 2000 sites, and Ramsar areas) covers territories characterized by the highest Ecological Value classes but still leaves significant portions outside protected areas.
RICHNESS AND RED LIST STATUS OF PLANT SPECIES
Data aggiornamento scheda:
Italy hosts a remarkable floristic heritage, both in terms of species and subspecies richness (2,815 lichens, 1,209 bryophytes, and 8,241 native vascular entities) and biogeographical value. Of the 8,241 Italian vascular plant,1,702 species (equal to 20.65%) are endemic, meaning they exist exclusively in the country. Among these, 1,128 species are regionally endemic, with their range restricted to a single Italian region (data updated to April 2024).
The indicator also highlights the IUCN risk status of 2,430 vascular plant entities (representing 29.5% of Italy’s vascular flora), identifying the main threats affecting them. Unfortunately, the overall conservation status cannot be considered satisfactory: 2.2% (54 species) of the 2,430 evaluated entities are extinct or likely extinct; 24.3% (590 species) are at risk of extinction.
Human-induced pressures related to land-use changes represent a major driver of plant species extinction risk. The Red List of vascular flora identifies the most critical pressures affecting species: Modification of natural systems (39% of the 2,430 assessed taxa are subject to this pressure);
Agricultural development (27%); Residential development (27%); Direct human disturbance in natural environments (20%).
WETLANDS OF INTERNATIONAL IMPORTANCE
Data aggiornamento scheda:
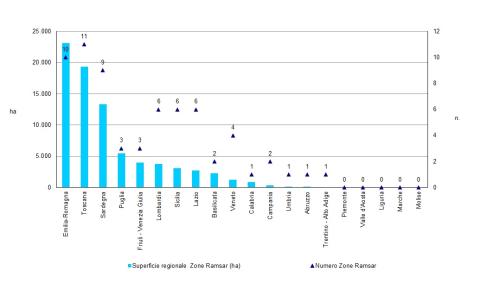
The Italian wetlands currently included in the official list of sites under the Ramsar Convention are 57, covering a total of 72,288 hectares. Additionally, three Ministerial Decrees were issued in 2011, 2013, and 2016 for the establishment of nine more areas. In total, the 66 Italian Ramsar sites (57 designated and 9 in the process of designation) are distributed across 15 regions, covering 79,826 hectares. The regions with the largest and most numerous areas are Emilia-Romagna (10 areas, 23,112 ha), Tuscany (11 areas, 19,306 ha), and Sardinia (9 areas, 13,308 ha).
The level of implementation of protection and management measures for these areas is not sufficiently known, despite being essential to ensure the conservation of habitats, flora, and fauna.