Panel 1
Sabrina Agnesi, Silvia Properzi, Susanna D'Antoni, Stefania Ercole
Both the number of protected areas and the extent of protected marine surface have steadily increased over time. At present, 30 Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) have been established in Italy, across 10 Italian regions, along with a further 10 areas protecting coastal marine stretches.
Sicily and Sardinia host the largest share of marine protected areas, both in terms of number and area of protected surface. Between 2012 and 2023, at the national level, the surface of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) increased by 3.1%, following the establishment in 2018 of the two MPAs of Capo Testa–Punta Falcone in Sardinia and Capo Milazzo in Sicily, and in 2023 of the Capo Spartivento MPA in Sardinia.
The indicator describes the surface area of Italian coastal waters subject to protection regimes. Specifically, it covers waters included within Marine Protected Areas (MPAs, established pursuant to Laws 979/1982 and 394/1991, as amended) and within other categories of protected areas listed in the Official List of Protected Areas (EUAP). All these surfaces are collectively referred to as “Marine Protected Areas”. The internationally designated Marine Natural Area known as the “Sanctuary for Marine Mammals” is not included in the calculation of protected surfaces.
To assess the level of protection of the marine environment, expressed through the surface area of Italian coastal waters falling within Marine Protected Areas (MPAs), established under Laws 979/1982 and 394/1991, as amended, and within other protected area categories listed in the Official List of Protected Areas (EUAP) that include marine protected surfaces.
L 979/82 (Provisions for the defense of the sea);
L 127/85 (Ratification and execution of the Protocol relating to specially protected areas of the Mediterranean); L 394/91 (Framework Law on Protected Areas) and subsequent amendments;
EUAP, 6th update (DM 27.04.2010 GU n. 125 of 31.05.2010);
Ministerial Decree 17/05/2018, n. 102. Establishment of the marine protected area «Capo Testa - Punta Falcone»;
Ministerial Decree 26/11/2018, n. 153. Approval of the disciplinary regulation of the marine protected area «Capo Milazzo» (published in the Official Gazette no. 55 of 6-3-2019).
Ministerial Decree 22/12/2023 n. 440 (published in the Official Gazette no. 245 of 18 October 2024) Establishment of the Capo Spartivento marine protected area.
Panel 2
-
The indicator provides quantitative information only and does not assess the level of implementation, the effectiveness of protection measures, or the environmental conditions of the protected areas.
Not foreseen.
Data quality assessment
MASE data - V EUAP (2003); MASE - VI EUAP (2010) and subsequent national or subnational laws and provisions establishing AA. PP.
Consultation of the Common Database on Designated Areas (CDDA), now merged into the Nationally Designated Areas (NatDA ) published on the website of the European Environment Agency ( https://cdr. eionet. europa. eu/help/cdda/ -( https://www. eea. europa. eu/data-and-maps/data/nationally-designated-areas-national-cdda-17)
National, Regional (10/20)
1986-2024
Indicator assessment
Collected data were represented in tabular and graphical form through computerized processing.
The time-based increase in the number of established Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) was calculated using the date of signature of the first establishment decree as the reference.
The protected marine surface has reached 311,463 hectares (Table 1). However, the status can only be considered medium, as most new designations fall within areas already included in the Natura 2000 Network, thus reducing the actual added value in terms of real expansion of marine protected surface.
The trend can be considered positive, as both the number of protected areas and protected marine surface have steadily increased over time. Between 2012 and 2023, at the national level, MPA surface increased by 3.1%, following the establishment in 2018 of the two MPAs of Capo Testa–Punta Falcone in Sardinia and Capo Milazzo in Sicily, and in 2023 of the Capo Spartivento MPA in Sardinia (Table 1).
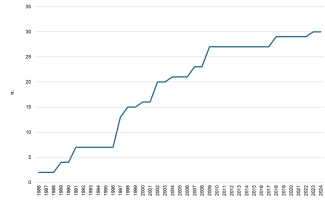
Sicily and Sardinia are the regions hosting the largest number of MPAs, both in terms of number (7 in Sicily and 8 in Sardinia) and protected marine surface (80,053 ha in Sicily and 93,674 ha in Sardinia, including the marine portion of the La Maddalena Archipelago National Park). In Sardinia, the Capo Spartivento MPA was recently established (2023 establishment decree). In Campania, the six MPAs cover a total surface area of 22,441 ha. In Lazio, the five MPAs extend over a total surface of 4,204 ha, which is much smaller compared to the situations described above, as three of these areas have very limited extensions (less than 10 ha). By contrast, in Tuscany, the mere presence of the Tuscan Archipelago National Park protects an area of almost 57,000 hectares (Table 1).
However, surface area alone does not allow assessment of the actual level of protection, which is closely linked to zoning distribution and management effectiveness.