Panel 1
Giovanni Braca, Robertino Tropeano
The indicator provides on an annual basis the assessment, expressed as a percentage, of the ratio between the annual volume of the runoff (surface preselling) and the annual volume of precipitation. This indicator aims to provide an assessment of the amount of water that is directly transformed into a surface runflow compared to total precipitation and to assess the trend over the long term, also in relation to the possible impact due to climate change. The annual values of the indicator shall also be compared with the corresponding average value calculated over the entire period 1951–2024.
In 2024, the value of the indicator was 26.1%, higher than the average value of 25.1% in the long term. This shows a trend reversal compared to 2023, in which there was a value of 23.7%, below the average. The comparison is even more marked with 2022, the year in which the indicator reached an all-time low of 18.5%.
The indicator evaluates the percentage ratio between the annual volume of surface runoff, i.e. the rate of precipitation that is directly transformed into a surface runoff, and the annual volume of precipitation summarised to the national territory. By runoff in particular we mean the rate of precipitation that does not be able to infiltrate the ground due to the saturation of the soil or the reduced infiltration capacity, flows on the surface of the ground until it reaches the hydrographic lattice producing the surface outflow.
Provide an assessment of the amount of water that turns into surface runoff in relation to total precipitation. The indicator is specifically defined to highlight possible impacts of climate change on the precipitation and outflow regime. The possible trend, purified of the effect of the change in the water-recognizing of the soils, could be an indication of a change in the extent and distribution of precipitation over the year.
There is no regulatory reference.
Panel 2
- Braca, G., Mariani, S., Lastoria, B., Tropeano, R., Casaioli, M., Piva, F., Marchetti, G., e Bussettini, M., 2024: Bilancio idrologico nazionale: stime BIGBANG e indicatori sulla risorsa idrica. Aggiornamento al 2023. Rapporti n. 401/2024, ISPRA, Roma. Disponibile online all’indirizzo: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/it/pubblicazioni/rapporti/bilancio-idrologico-nazionale-stime-bigbang-e-indicatori-sulla-risorsa-idrica-aggiornamento-al-2023.
- Braca, G., Mariani, S., Lastoria, B., Piva, F., Archi, F., Botto, A., Casaioli, M., Forte, T., Marchetti, G., Peruzzi, C., Tropeano, R., Vendetti, C., e Bussettini, M., 2023: Bilancio idrologico nazionale: focus su siccità e disponibilità naturale della risorsa idrica rinnovabile. Aggiornamento al 2022. Rapporti n. 388/2023, Roma. Disponibile online all’indirizzo:
- https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/it/pubblicazioni/rapporti/bilancio-idrologico-nazionale-focus-su-siccita-e-disponibilita-naturale-della-risorsa-idrica-rinnovabile-aggiornamento-al-2022.
- Braca, G., Bussettini, M., Lastoria, B., Mariani, S., e Piva, F., 2021: Il Bilancio Idrologico Gis BAsed a scala Nazionale su Griglia regolare – BIGBANG: metodologia e stime. Rapporto sulla disponibilità naturale della risorsa idrica. Rapporti n. 339/21, Roma. Disponibile online all’indirizzo: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/it/pubblicazioni/rapporti/il-bilancio-idrologico-gis-based-a-scala-nazionale-su-griglia-regolare-bigbang.
- SNPA, 2024: Il clima in Italia nel 2023. Report SNPA n. 42/2024. Disponibile online all’indirizzo: https://www.snpambiente.it/snpa/il-clima-in-italia-nel-2023/.
- SNPA, 2023: Il clima in Italia nel 2022. Report SNPA n. 36/2023. Disponibile online all’indirizzo: https://www.snpambiente.it/2023/07/20/il-clima-in-italia-nel-2022/.
- SNPA, 2021: Rapporto sugli indicatori di impatto dei cambiamenti climatici – Edizione 2021. Report SNPA n. 21/2021. Disponibile online all’indirizzo: https://www.snpambiente.it/2021/06/30/rapporto-sugli-indicatori-di-impatto-dei-cambiamenti-climatici-edizione-2021/.
The indicator is built at the annual scale from estimates of runoff and precipitation at the monthly scale made with the BIGBANG national hydrological budget model, version 9.0, of ISPRA based on official data produced at national and local level. Such time aggregations shall not take into account the effect of the precipitation intensity affecting infiltration and runoff. In addition, previously published estimates of the BIGBANG model may have slight deviations from the estimates of the latest version available as some data or schematizations underlying the model may be improved. Correct comparisons between the values of the indicator must therefore be made using the same version of the BIGBANG model.
A daily scale indicator processing would allow to adequately grasp the effect of the precipitation intensity on the infiltration of the soils and on the runoff.
Data quality assessment
ISPRA
JRC (Joint Research Centre)
Regional hydro-meteorological services and autonomous provinces
The precipitation and temperature data used are mostly those collected and published by the regional and provincial structures to which, according to Article 92 of Legislative Decree no. 112 of 31 March 1998, the functions and tasks of the peripheral offices of the National Hydrographic and Tire Service (SIMN, now merged into ISPRA) of the Department for National Technical Services, were transferred. The precipitation data are collected directly from the regional structures and autonomous provinces, while for the temperature are used the maps produced under the SCIA system of ISPRA (https://scia.isprambiente.it). The precipitation and temperature data aggregated to the monthly scale on the regular BIGBANG grid of resolution 1 km, which covers the entire national territory, are available on the Groupware portal of ISPRA (https://groupware.sinanet.isprambiente.it/bigbang-data/library/bigbang-90). The data on the hydraulic characteristics of the soils are accessible (subject to registration) to the JRC/ESDAC portal (http://esdac.jrc.ec.europa.eu/content/lucas-2009-topsoil-data). For the permeability data of hydrogeological complexes, a new permeability paper produced by ISPRA was used compared to previous years.
national
1951–2024
Indicator assessment
The estimate of the indicator series from 1951 to 2024 is carried out through the national model of hydrological budget on a monthly scale developed by ISPRA, called BIGBANG-Billionological Impact Gis BAsed on a National Scale on Regular Grid, version 9.0, which evaluates the runoff as the end of the hydrological soil balance with the Thornthwaite and Mather method and the precipitation as a spatial interpolation of data recorded by the networks.
The indicator is calculated from the monthly evaluation of the runoff and precipitation on a regular grid of 1 km resolution that covers the entire national territory and aggregated to the annual scale. For the year i-th, the IRFi indicator (in %) is calculated as the ratio of the annual RFI runoff to the annual TPi precipitation:
IRFi = (RFi/TPi) x 100.
In 2024 the runoff index was 26.1% and is higher than the long-term 1951–2024 average, or 25.1%. This means that only 26.1% of the total annual precipitation (estimated at 318.8 billion cubic meters) has directly turned into surface runflow (83.3 billion cubic meters).
In terms of assessing the amount of water that turns into surface runoff in relation to total precipitation, resulting in the runoff index above the long-term average, the state in 2024 can be defined as positive as it indicates greater availability of surface water resources.
The runoff index has a slight, statistically significant trend based on the Mann-Kendall test, with a significance level of 5%. The indicator takes into account the effect of the temporal variability of the soil sealing.
The trend of the indicator is attributable to two factors, the increase in temperature and the waterproofing of the soils, which act in the opposite direction. On the one hand, the average temperature has an increasing trend, due to climate change, which produces, due to the consequent increase in the share of evapotranspiration, a reduction in the availability of renewable water (internal flow) and therefore the rate of precipitation that turns into runoff. The national series of average temperature anomalies, compared to the average value over the 30-year climate 1991–2020, shows a significant increase in recent decades. At the national level, 2024 was the hottest year since 1961 (+1.33 C) and the eleventh consecutive year with a positive anomaly compared to the climatological average of the last thirty years of reference. On the other hand, the increase in the waterproofing of the soils produces the opposite effect on the runoff.
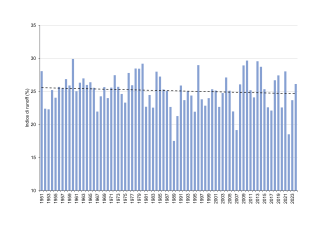
The runoff index, in the period 1951–2024, varies between a minimum value of 17.5%, estimated for 1989, and a maximum value of 29.9%, estimated for 1960 (Figure 1). This means that, from 1951 to 2024, no more than 30% of the annual precipitation in Italy has turned into surface runoff, to which must be added the basic outflow, deriving from underground water circulation, to obtain the total annual runoff in watercourses.
In 2024, the runoff index (26.1%) recorded a temporary reversal of the trend compared to 2023, the year in which it was equal to 23.7% and below the long-term average (25.1%), and compared to 2022, in which the deviation was even greater from the average resulting in the index of 18.5% (second value smaller than the series after the 1989 low).
Analyzing the historical series of the long-term runoff index remains, however, a negative trend to be attributed to the increase in temperature that involves a reduction in the natural availability of renewable water resources (see the "Internal Flow" indicator present in the Environmental Theme "Water sources and Balance" of the Environmental Indicators Database) of which the runmanship constitutes a rate.
The series of values of the components of the hydrological balance, and therefore also of the runoff index, are recalculated every year on the basis of new data sets and new schematizations, so a correct comparison in time and space must be made with respect to the same version of the model.