Panel 1
Giorgio Cattani, Mariacarmela Cusano, Alessandro Di Menno di Bucchianico, Raffaela Gaddi, Alessandra Gaeta, Giuseppe Gandolfo, Gianluca Leone
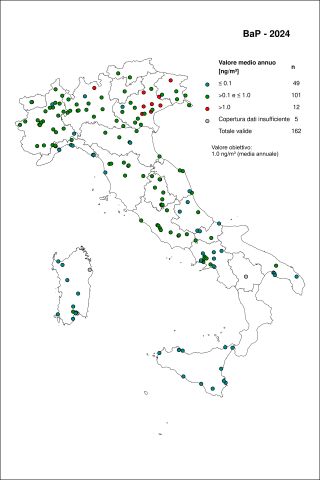
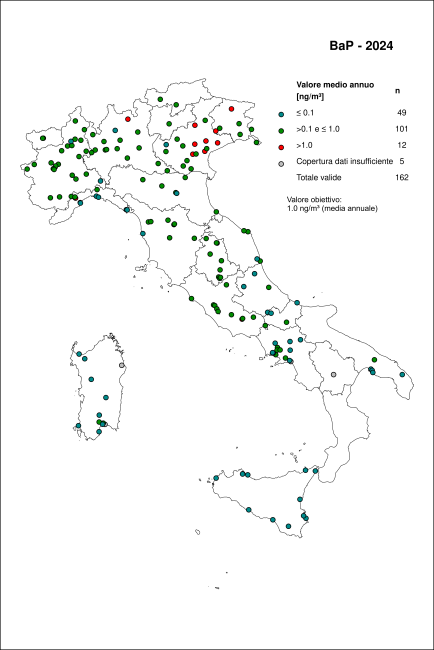
The indicator is based on atmospheric concentration data of benzo(a)pyrene measured in 2023 at monitoring stations distributed across the national territory, collected and archived by ISPRA in the InfoAria database, in accordance with Directive 2008/50/EC (and its national transposition, Legislative Decree 155/2010) and Commission Implementing Decision 2011/850/EU. A total of 164 monitoring stations measured and reported B(a)P data. Among these, 159 provided time series with sufficient temporal coverage for the verification of reference values. Exceedances of the target value were recorded at 17 stations, corresponding to 10.7% of the cases.
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) are produced during the incomplete combustion of organic materials and are released into the atmosphere almost entirely adsorbed onto particulate matter. Many PAH compounds are carcinogenic, although establishing carcinogenicity for individual PAHs in humans is extremely challenging, as real-world exposures involve complex mixtures of dozens of PAHs. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC, 2012) has classified benzo(a)pyrene (B(a)P), in particular, as a Group 1 carcinogen for humans.
B(a)P is considered a reliable indicator of carcinogenic risk within the PAH class. It has been estimated that lifelong exposure to an average concentration of 1 ng/m³ of B(a)P results in an incremental risk of 9 cases of lung cancer per 100,000 individuals. The World Health Organization (WHO) has therefore recommended a guideline value of 1 ng/m³ as the annual average concentration for B(a)P. This value aligns with the target value set by Legislative Decree 155/2010.
The indicator was developed based on atmospheric concentration data of B(a)P measured in 2023 at monitoring stations across the national territory, collected in the InfoAria database in accordance with Commission Implementing Decision 2011/850/EU. The annual mean concentration was calculated as the key metric to assess compliance with the target value established by the reference legislation (Legislative Decree 155/2010 and subsequent amendments) for the protection of human health.
To provide information on the state of air quality through statistical parameters calculated from ambient benzo(a)pyrene (B(a)P) concentration data, verifying compliance with the regulatory target values and comparing the results with the reference levels established by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Directive 2004/107/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 15 December 2004 on arsenic, cadmium, mercury, nickel, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in ambient air
Legislative Decree 155/2010 – Legislative Decree of 13 August 2010, No. 155, implementing Directive 2008/50/EC on ambient air quality and cleaner air for Europe (Official Gazette No. 216 of 15/09/2010 – Ordinary Supplement No. 217 – in force since 30/09/2010)
Commission Implementing Decision 2011/850/EU of 12 December 2011 laying down provisions for the implementation of Directives 2004/107/EC and 2008/50/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the reciprocal exchange and reporting of ambient air quality information [notified under document C(2011) 9068]
The objective of Directive 2008/50/EC is to enable the assessment of ambient air quality on a harmonized basis, to obtain information on air quality status in order to combat atmospheric pollution, to ensure public availability of information, and to promote cooperation among Member States.
Directive 2004/107/EC established a target value for the concentration of arsenic, cadmium, nickel, and benzo(a)pyrene in ambient air to avoid, prevent, or reduce the harmful effects of exposure to these substances on human health and the environment.
Legislative Decree 155/2010 transposes Directive 2008/50/EC and replaces the national provisions implementing Directive 2004/107/EC (previously transposed by Legislative Decree No. 152 of 3 August 2007, repealed upon the entry into force of Legislative Decree 155/2010), establishing a unified regulatory framework for the assessment and management of ambient air quality. It also aims to enable regions and autonomous provinces to carry out air quality assessment and management.
The limit values set by Legislative Decree 155/2010 represent ambient air quality objectives to be pursued to avoid, prevent, and reduce harmful effects on human health and the environment. The WHO reference values serve as guidance for reducing the health impact of air pollution. The regulatory target value for B(a)P in ambient air is 1.0 ng/m³ as an annual mean concentration, which coincides with the guideline value recommended by WHO. Specifically, as established by the applicable legislation, the target value refers to the total B(a)P content in the PM10 fraction of particulate matter, calculated as an annual average over a calendar year.
Panel 2
IARC (2012). A review of human carcinogens. Part F: Chemical agents and related occupations / IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans (2009: Lyon, France) IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans ; v. 100F.
ISPRA, Annuario dei dati ambientali, various editions
SNPA (2024) La qualità dell'aria in Italia. Ed. 2023
WHO-World Health Organisation (2000). Air quality guidelines for Europe; second edition. Copenhagen, WHO Regional Office for Europe Regional Publications
Data quality assessment
Autonomous Provinces, Regions, SNPA (National System for Environmental Protection)
ISPRA, Database InfoAria
National;
Regional (19/20);
Provincial (76/110);
Municipal (139/8047)
2023
Indicator assessment
The indicator is based on atmospheric B(a)P concentration data measured at monitoring stations distributed across the national territory, collected and archived by ISPRA in the InfoAria database in accordance with Commission Implementing Decision 2011/850/EU. The annual mean concentration was calculated following European standards to enable comparison with the target value for the protection of human health established by the reference legislation (Legislative Decree 155/2010). For this comparison (Figure 2), only data series with a minimum temporal coverage of 33% (excluding gaps due to routine calibration or maintenance) or 14% with an even distribution of data throughout the year were used, in accordance with the specific criteria for benzo(a)pyrene outlined in the annex to Legislative Decree 155/2010.
The target value (1.0 ng/m³) was exceeded at 17 monitoring stations, representing 10.7% of the cases (Table 1 and Figure 2).
In 2023, exceedances of the target value occurred primarily in areas such as the Po Valley, the foothills of the Apennines and the Alps, and the Sacco Valley in southern Lazio, where residential wood biomass consumption is high and winter meteorological conditions promote pollutant accumulation. Exceedances observed in the Savona area (Liguria) are instead attributable to industrial emission sources.
Data
Tabella 1: B(a)P - Stazioni di monitoraggio: dati e parametri statistici per la valutazione della qualità dell'aria (2024)
Elaborazione ISPRA su dati SNPA
“1” tipo di zona: U = URBANA; S = SUBURBANA; R = RURALE
“2” tipo di stazione: T = TRAFFICO; F = FONDO; I = INDUSTRIALE
"3" in grassetto sono riportati i dati relativi alle serie con copertura sufficiente nel rispetto dei criteri dell'Allegato I, D.Lgs. 155/2010
4 - copertura minima ai sensi del D.Lgs. 155/2010, Allegato I: almeno il 33% di dati validi per le misurazioni in siti fissi, al netto delle perdite dovute a taratura, periodica o manutenzione ordinaria; almeno il 14% per le misurazioni indicative, se i dati sono uniformemente distribuiti nel corso dell'anno
Tabella 2: B(a)P - Classificazione delle zone rispetto alle soglie di valutazione e verifica della presenza di superamenti del valore obiettivo ai sensi del D.Lgs.155/2010 (2024)
Elaborazione ISPRA su dati SNPA
zona: parte del territorio nazionale delimitata, ai sensi del D.Lgs 155/2010, ai fini della valutazione e della gestione della qualità dell'aria ambiente;
agglomerato: zona costituita da un'area urbana o da un insieme di aree urbane che distano tra loro non più di qualche chilometro oppure da un'area urbana principale e dall'insieme delle aree urbane minori che dipendono da quella principale sul piano demografico, dei servizi e dei flussi di persone e merci, avente: 1) una popolazione superiore a 250.000 abitanti oppure; 2) una popolazione inferiore a 250.000 abitanti e una densità di popolazione per km 2 superiore a 3.000 abitanti;
Superamento VO annuale: Si intende superato qualora sia stato determinato il superamento in almeno una stazione di monitoraggio collocata nel territorio della zona.
Classificazione: aboveUAT: superiore alla soglia di valutazione superiore (60% del valore obiettivo, 0,6 ng/m³) LAT-UAT : compresa tra la soglia di valutazione inferiore e la soglia di valutazione superiore belowLAT : inferiore alla soglia di valutazione inferiore (40% del valore obiettivo, 0,4 ng/m³) nota: Il superamento delle soglie di valutazione superiore e delle soglie di valutazione inferiore deve essere determinato in base alle concentrazioni degli inquinanti nell'aria ambiente nei cinque anni civili precedenti. Il superamento si realizza se la soglia di valutazione è stata superata in almeno tre sui cinque anni civili precedenti.
Max media annua: valore più alto della media annuale registrato nella zona
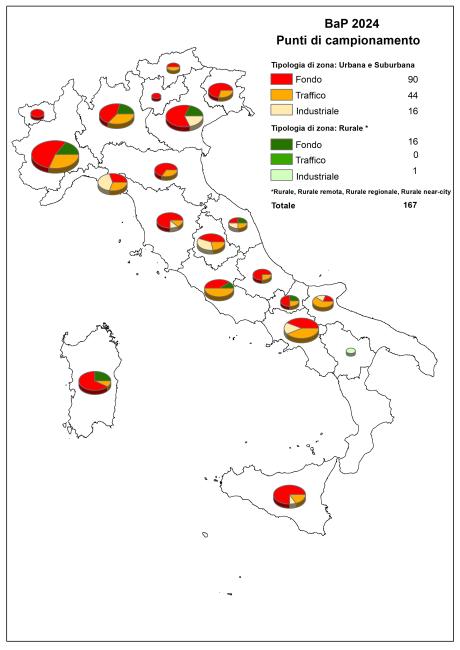
A total of 164 monitoring stations measured and reported B(a)P data. Of these, 159 stations (97% of the total) had a minimum temporal data coverage of 33% (excluding data losses due to periodic calibration or routine maintenance) or 14%, with a uniform data distribution over the year, in accordance with the specific criteria for benzo(a)pyrene outlined in the annex to Legislative Decree 155/2010. The classification of B(a)P monitoring stations according to macroscale siting criteria defined by legislation is shown in Figure 1.
The entire national territory is divided into zones and agglomerations for the purpose of ambient air quality assessment as stipulated by Legislative Decree 155/2010. Each zone is classified based on the threshold criteria established in the same decree, as outlined in Table A.
This classification is critical, as it determines the related assessment obligations and is generally updated every five years.
If an exceedance of a limit value is observed at even one monitoring station within the year, the entire zone is considered in exceedance.
In 2023, exceedances of the target value were recorded in 13 out of 77 zones, distributed across 6 regions and one autonomous province (Table 2).