Irma Lupica
In 2023, the quantity of municipal waste incinerated—including Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF), dry fraction, and bio-dried material derived from municipal waste treatment—amounted to 5.5 million tonnes, marking a 4% increase compared to 2022. Of this total, 72.7% was processed in Northern Italy, 9.1% in Central Italy, and 18.2% in the South.
The incineration infrastructure is predominantly concentrated in the North, which hosts 25 operational plants, whereas the Central and Southern regions operate 5 and 6 facilities, respectively.
An incineration plant is defined as any fixed or mobile technical unit and equipment designed for the thermal treatment of waste, with or without energy recovery from the combustion process. This indicator measures both the number of incineration plants and the quantity of municipal waste they process.
The indicator allows comparisons across different territorial contexts (municipality/province/region) and supports decision-making processes and environmental policies. It also helps assess the impact of human activities.
The key directive on waste incineration is Directive 2010/75/EU of the European Parliament and Council, dated November 24, 2010, on industrial emissions (integrated pollution prevention and control), known as the Industrial Emission Directive (IED). This directive consolidated and revised seven previous EU directives into a single legislative framework.
At the national level, the directive was implemented through Legislative Decree No. 46 of March 4, 2014, which introduced modifications to Legislative Decree No. 152/2006 ("Environmental Code"). Specifically, Title III-bis of Part IV of Legislative Decree 152/06 concerns waste incineration and co-incineration.
Additionally, Commission Decision 2019/2010/EU established conclusions on the Best Available Techniques (BAT) for waste incineration, serving as a reference for setting permit conditions, including emission limits under normal operating conditions for installations subject to Chapter II of Directive 2010/75/EU (Integrated Environmental Authorization - AIA).
ISPRA - Rapporto rifiuti urbani - Edition 2023
Modello Unico di dichiarazione Ambientale MUD ISPRA - Catasto rifiuti (http://www.catasto-rifiuti.isprambiente.it).
National, Regional
2002-2023
The indicator measures the quantity of incinerated municipal waste in Italy. The data includes non-recyclable municipal waste, dry fraction, RDF, and bio-dried waste derived from municipal waste treatment. The information is sourced from the Environmental Declaration Form (MUD), submitted by entities identified under Article 189, Paragraph 3, of Legislative Decree No. 152/2006 to the relevant Chambers of Commerce, Industry, Handicrafts, and Agriculture.
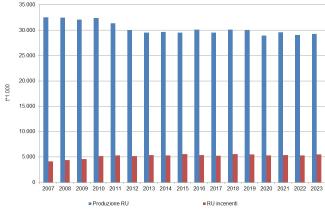
In 2023, a total of 5.5 million tonnes of municipal waste were incinerated. Of this, 48.7%—approximately 2.7 million tonnes—consisted of unprocessed municipal waste (classified under Chapter 20 of the European Waste Catalogue), while the remaining portion—over 2.8 million tonnes—comprised waste resulting from municipal waste treatment processes, such as Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF), dry fraction, and, to a lesser extent, bio-dried material (Table 2). A total of 36 incineration facilities were operational across the national territory (Table 3).
Table 3 shows that, between 2008 and 2023, the number of incineration plants decreased by 13 units. This reduction was particularly pronounced in Central Italy, where 8 facilities ceased operations. Over the same period, however, the volume of incinerated waste progressively increased by 26.3%. This trend is explained by the fact that, wherever technically feasible, facilities operated at or near their thermal load capacity, thus maximizing throughput (Table 1).
| Allegati |
|---|
Titolo
Table 1: Municipal waste incinerated by region Fonte
ISPRA |
Titolo
Table 2: Waste incinerated in municipal plants by type of waste (2023) Fonte
ISPRA Legenda
RU: Municipal waste; |
Titolo
Table 3: Number of incineration plants for municipal waste, dry fraction (DF), and solid recovered fuel (SRF) Fonte
ISPRA Legenda
a Includes a plant in Colleferro that treated very small amounts of waste for a short period before being shut down. |
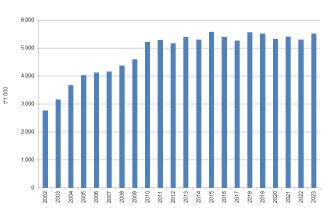
In 2023, the total quantity of municipal waste incinerated—including Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF) and waste derived from the treatment of municipal waste—reached 5.5 million tonnes, reflecting a 4% increase compared to 2022 (Table 1 and Figure 1). Of this amount, 72.7% was treated in Northern Italy, 9.1% in Central Italy, and 18.2% in the South.
Compared to the previous year, municipal waste incineration increased by 213,000 tonnes in 2023. This growth was entirely concentrated in the North (+5.9%), while quantities remained stable in the Center and decreased by 1% in the South—equivalent to a reduction of approximately 10,000 tonnes.
A total of 36 incineration plants were operational across Italy in 2023, with 25 located in the North, 5 in the Center, and 6 in the South. Notably, Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna hosted 12 and 7 plants, respectively, and together processed approximately 3 million tonnes of municipal waste. This accounts for 73.6% of the incinerated waste in Northern Italy and 53.5% of the national total (Tables 1 and 3).