Panel 1
Costanza Mariotta, Jessica Tuscano
Under the pressure of community policies, the flow of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) has assumed a role of primary importance within the waste cycle for the implementation of the principles of the circular economy, also for the purposes of the supply of Critical Raw Materials. Compared to waste in general, WEEE is characterized by the presence within it of both dangerous substances and materials with high economic value. The legislative provisions have therefore established measures aimed at protecting the environment and human health by preventing or reducing the negative impacts deriving from the design, production of electrical and electronic equipment and the production and management of waste resulting from them. The recycling industry becomes fundamental for the transition towards the circular economy: in fact, it allows material flows deriving from waste recovery to be reintroduced into production cycles, increasing the efficiency of resources to achieve sustainable development objectives and avoiding the importation of raw materials. Given an overall collection of WEEE equal to approximately 510 thousand tonnes in 2023, the percentage of preparation for reuse and recycling is equal to 84.2% and that of overall recovery is 93.9%.
The indicator measures the ratio between the quantities of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) recycled, including those prepared for reuse through control, cleaning, dismantling and repair operations, compared to the total quantity of waste collected, both from domestic and professional sources. Domestic WEEE originates from private households and also includes that of commercial, industrial, institutional and other types of origin which is similar, in nature and quantity, to that originating from private households; professional WEEE is all waste not coming from households. Electrical and electronic equipment includes a wide range of devices such as mobile phones, computers, televisions, refrigerators, household appliances, lamps, but also medical devices and photovoltaic panels. With the continuous expansion of the market and the shortening of innovation cycles which make the equipment obsolete after just a few months, the equipment itself is replaced more and more quickly, contributing to increasing the flow of EEE waste in quantitative terms. Furthermore, modern electronics contain within them both dangerous substances as well as materials of high economic value and critical raw materials, strategic for many industrial productions. Their incorrect management can therefore determine impacts on human health and the environment as well as economic repercussions; on the other hand, guaranteeing the closure of the value chain through a homogeneous, widespread and effective collection network throughout the national territory, and adequate treatment of WEEE which allows the re-inclusion of recycled materials into production cycles, can increase resource efficiency and support the transition to a circular economy as well as contribute to the supply of critical raw materials.
Monitor progress towards a circular economy in the thematic area "waste management". The circular economy is based on the optimization of resources achievable through eco-design strategies that guarantee greater durability, reusability, possibility of upgrading and repairability of products, greater use of recycled materials and greater recyclability when they reach the end of their life, with a consequent reduction in environmental impacts and waste produced.
Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 19 November 2008 on waste.
Directive 2012/19/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 4 July 2012 on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE).
Legislative decree 3 April 2006, n. 152 Environmental regulations.
Legislative decree 14 March 2014, n. 49 Implementation of Directive 2012/19/EU on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE), which establishes measures and procedures aimed at protecting the environment and human health by: a) preventing or reducing the negative impacts deriving from the design and production of electrical and electronic equipment and from the production and management of waste electrical and electronic equipment; b) reducing negative impacts and improving the effectiveness of the use of resources to achieve sustainable development objectives.
Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2017/699 of 18 April 2017, defining a common methodology for calculating the weight of electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) placed on the market of each Member State and a common methodology for calculating the quantity by weight of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) generated in each Member State.
Commission Implementing Decision 2019/2193 of 17 December 2019 establishing the modalities for the calculation, verification and reporting of data and defining the formats for the submission of data for the purposes of Directive 2012/19/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council on waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE).
Panel 2
No limitations
None
Data quality assessment
ISPRA
Use the information contained in the database of annual environmental declarations (MUD) made by entities obliged under current legislation, which are not accessible to the public.
National
2019-2023
Indicator assessment
The indicator is expressed as a percentage and is obtained from the ratio between the quantity of recycled or recovered WEEE and the quantity of overall WEEE collected, both from domestic and professional sources. The indicator includes hazardous and non-hazardous waste.
The amount of recycled WEEE, also including that subjected to preparation operations for reuse, is calculated as the quantity of waste sent for recycling operations in treatment plants located in the national territory, added to the quantity of exported waste destined for recycling operations abroad, and excluding waste imported from abroad and recycled in national plants. The recovered waste also includes waste destined for energy recovery operations.
The information base is made up of the environmental declarations (MUD) presented annually by the obliged entities pursuant to art. 189 of Legislative Decree 152/2006.
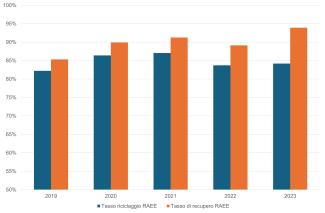
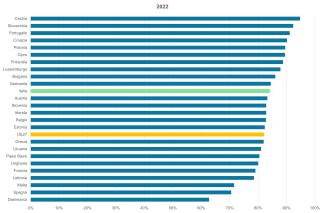
In 2023, approximately 84.2% of the waste collected was recycled or prepared for reuse through inspection, cleaning, disassembly and repair operations. The total WEEE recovered represents 93.9% (Table 1). At a European level, Italy ranks eleventh among countries, with 2 percentage points above the European average (82.2%, Figure 3).
The status of the indicator can be defined as good : over three quarters of the waste collected and sent for treatment are subject to recycling operations.
The trend in the recycling rate in the three-year period 2019-2021 is positive, going from 82.2% in 2019 to 87.1% in 2021. In 2022, given an increase in both the quantities collected and those recycled, the recycling percentage stands at 83.7%. This trend is correlated to a more marked increase in the quantities collected compared to 2021 (+6.3%) and a more limited increase in the quantities recycled (+2.2%). In 2023, however, there will be a decline in the quantities collected (-4.6%) and those recycled (-4%); the recycling percentage stands at 84.2%.
It is necessary to increase the collection of WEEE which, in 2023, still represents only 26% of the amount placed on the market (Table 1).
Data
Table 1: Quantities of electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) placed on the market and of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) collected, treated, recovered, and recycled
ISPRA
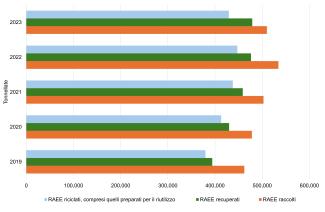
WEEE represents one of the main waste flows subject to monitoring taking into account the intrinsic characteristics of the products from which they derive, containing both dangerous substances, which require particular precautions in subsequent management, and materials with high economic value which can be reinserted into production cycles also for the purposes of supplying Critical Raw Materials. The quantity of electrical and electronic equipment placed on the market continues to grow also in quantitative terms, reaching almost 2 million tonnes in 2023 (+37.9% compared to 2019). The collection, which still represents only 26% of what is placed on the market, amounts to 510 thousand tonnes (+10.4% compared to 2019, Table 1 and Figure 1). 84.2% of the WEEE collected, approximately 429 thousand tonnes (+13% compared to 2019), was subjected to recycling operations, including preparation for reuse through inspection, cleaning, dismantling and repair. The treatment is mostly carried out in plants located on Italian territory: the WEEE exported for recycling purposes amounts, in fact, to just over 3 thousand tonnes. The overall recovery, which includes energy recovery, represents 93.9% of the total WEEE collected (479 thousand tonnes) (Table 1 and Figure 2).