Panel 1
Eugenia Bartolucci, Chiara Fiori, Luigi Marangio
For 62% of the sites, at least one surface area data (administrative or technical) is available. The sites for which the administrative surface area is known are 21,711, equal to 56% of the proceedings. Among the ongoing procedures, 59% of sites are in the notification phase, 21% are developing or have developed the conceptual model, while 20% have approved interventions.
For 97% of the sites with ongoing remediation processes, the state of contamination is known: 6,400 are potentially contaminated, 3,974 are contaminated and 5,502 are awaiting analytical investigations. Among the completed proceedings, only in 30% of cases was intervention necessary, while in the remaining 70% the proceedings were closed without interventions.
The indicator provides information on sites undergoing regional remediation procedures based on data extracted from the registries/databases of the regions/autonomous provinces/ARPA/APPA for the population of MOSAICO, the national information system on sites undergoing remediation procedures created by ISPRA within the framework of the National Environmental Protection System (SNPA) with the participation of Regions and Autonomous Provinces and managed by ISPRA. Procedures falling within Sites of National Interest (SIN) are excluded from the analysis and are represented by a specific indicator.
The indicator provides information on the number of sites registered in each registry/database, distinguishing those with ongoing procedures from those with concluded procedures, on the progress of procedure management, on how procedures concluded (with or without remediation), on the surface areas involved, on the contamination status, and on the types of intervention adopted (remediation, permanent safety measures - MISP, operational safety measures - MISO, mixed intervention).
Progress in the management of sites with ongoing remediation procedures is represented according to three phases: notification, conceptual model (characterization and any risk analysis), intervention including approved projects, ongoing interventions, and completed interventions awaiting certification or with partial certification.
Surface information has been provided as "administrative" and/or "technical" surface. The "administrative" surface refers to the entire area subject to administrative procedure (i.e., the sum of the involved cadastral parcels). The "technical" surface (equal to or smaller than the administrative surface) represents the area potentially impacted from an environmental perspective. The technical surface may vary, generally decrease, with the progress of the procedure due to improved knowledge.
The state of contamination is represented according to four categories: sites awaiting investigations, potentially contaminated sites, contaminated sites, non-contaminated sites. The first two refer to an ongoing "finding" phase, the state of contamination "contaminated site" indicates the actual and compelling need for a remediation intervention, while non-contaminated sites are those found to be so following investigations or following remediation interventions.
The indicator also provides a focus on ongoing and completed remediation procedures that have passed the approval phase of the site characterisation plan and are therefore associated with greater environmental significance.
To provide information on contaminated sites registered by the regions/autonomous provinces in their own registries/databases and, more generally, on sites undergoing remediation procedures, on the progress in their management, contamination status, and areas involved.
The management of contaminated sites is regulated in Italy by Legislative Decree 152/06 and subsequent amendments (Part IV, Title V). Legislative Decree 152/06 identifies risk analysis as the key tool for the definition and management of contaminated sites.
Article 251 of the Legislative Decree provides that regions and autonomous provinces shall prepare the registry of sites to be remediated, which must include a list of sites undergoing remediation and environmental restoration interventions, the identification of the responsible parties for the remediation, and the public entities that the region intends to use in case of default by the obligated parties, for the purpose of executing the remediation ex officio.
The current regulation sets conditions for the conclusion of the procedure, which in the case of contaminated sites consists of achieving the remediation objectives. However, it does not establish time limits for the achievement of specific procedural or remediation milestones.
Panel 2
2025, ISPRA. The status of remediation of contaminated sites in Italy: fourth report on regional data. Report 424/2025
2025, ISPRA. The status of remediation of contaminated sites in Italy: third report on regional data. Report 409/2025
2023, ISPRA. The status of remediation of contaminated sites in Italy: second report on regional data. Report 387/2023
2022, ISPRA, Environment in Italy: an overview, Environmental data yearbook 2022
2017, ISPRA. Environmental data yearbook – 2017 edition
Despite the constant updating of data, as of the reference date it is still not possible to provide a complete picture of the state of contamination and the progress of remediation efforts in Italy. Gaps persist due to the lack of integration and overlap of data related to procedures falling within Sites of National Interest (SIN) and those managed at the local level by the respective regions and autonomous provinces. Furthermore, the Sardinia region is not included in the analyses, as it has never contributed to the population of the MOSAICO system; the latest available data are outdated (updated as of 12/31/2019) and aggregated at the municipal level rather than by individual procedure.
In order to overcome these limitations and improve the quality of information, the following actions are necessary:
- Acquisition of updated data for Sardinia: Integrating the missing information will make it possible to complete the overview of regional sites.
- Extension of surface data: Collect data related to the administrative and technical extension of sites for procedures currently lacking this information.
- Definition of contamination status: Determine the contamination status for procedures that are currently unclassified.
Data quality assessment
-
ISPRA → Italian Institute for Environmental Protection and Research
-
SNPA → National System for Environmental Protection
-
Regioni e Province Autonome → Regions and Autonomous Provinces
MOSAIC - SNPA database of sites subject to remediation proceedings. Https://mosaicositicontaminati. isprambiente. it/index. html
National (I); Regional (R 19/20)
2016-2023
Indicator assessment
The progress in the management of sites undergoing procedures is expressed in terms of the number of sites found in each of the following three phases:
“Notification”: refers to the initial procedural phase consisting of the start of the process.
“Conceptual Model”: the conceptual model of the site is formulated, both in terms of verifying the presence and quantifying the contamination in environmental matrices, and in terms of defining the critical source-pathway-target routes on which to intervene in the possible remediation/operational safety (MISO)/permanent safety (MISP) phase.
“Remediation”: includes the procedural steps ranging from the approval of a remediation/MISO/MISP intervention to its conclusion pending certification.
The definition of the contamination status of the sites is divided into four possible scenarios:
- In the sites in the notification phase, the contamination status is classified as “pending analytical verification”;
- Following the execution of preliminary investigations and/or the characterization plan, the comparison with tabular screening values (CSC - contamination threshold concentrations) for soil and groundwater matrices leads to the identification of potentially contaminated sites (C>CSC – risk threshold concentrations); in some situations, especially for groundwater or in the case of applying simplified procedures, the exceeding of these tabular limits can lead to the designation of the site as contaminated;
- Subsequently, through the site-specific risk analysis that establishes new threshold values (CSR), the site may be declared contaminated (C>CSR) or not contaminated (C<CSR);
- Finally, a contaminated site is declared not contaminated following the positive conclusion of the intervention.
For the management of sites confirmed as contaminated, the legislation provides for the following interventions:
- Operational safety (MISO): interventions carried out on a site with ongoing activity aimed at ensuring an adequate level of safety for people and the environment, pending further permanent safety or remediation interventions to be carried out upon the cessation of activity; it also includes contamination containment measures to be implemented temporarily until remediation or permanent safety is carried out, in order to prevent the spread of contamination within the same matrix or among different matrices;
- Permanent safety (MISP): interventions aimed at definitively isolating the pollution sources from surrounding environmental matrices and ensuring a high and definitive level of safety for people and the environment; in such cases, monitoring and control plans must be provided, as well as use restrictions compared to urban planning instruments;
- Remediation: interventions aimed at eliminating pollution sources and pollutants or at reducing their concentrations in soil, subsoil, and groundwater to a level equal to or lower than the risk threshold concentrations (CSR).
The areas affected by the procedures are indicated in hectares (ha) and are accompanied by the percentage of sites for which such information is available relative to the total number of registered sites.
The number of proceedings registered is equal to 38,556, of which 16,365 proceedings are in progress (equal to 42% of all proceedings) and 22,191 concluded (58%) (Table 1).
A comparison between the data updated to 2023 and those to 2021 shows an increase in the total number of proceedings of 1,742 units (+5% of the total number of proceedings in 2021), resulting from a decrease in ongoing proceedings of 975 and an increase of 2,717 completed proceedings (Figure 1). The changes recorded depend both on the start of new procedures in the two-year period 2022-2023 and on the verification and updating of the registers/databases carried out in the same period period and finally by the lack of data from the Sardinia region which may lead to an underestimation of the recorded variation compared to the real one.
In fact, 2,593 procedures activated in the two-year period 2022-2023 (Table 6), of which 1,082 were concluded in the same two-year period.
The data relating to the number of proceedings in 2022 (Figure 1) are estimated on the basis of information relating to the activation and closure dates of the proceedings updated to 2023.
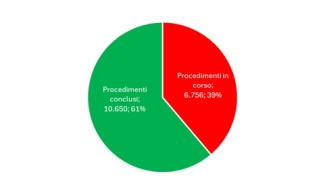
The total number of reclamation procedures of interest from an environmental point of view is 17,406, equal to approximately 45% of the total procedures (38,556). Of these, 6,756 (equal to approximately 39%) are underway and 10,650 (equal to approximately 61%) have been completed (Figure 5).
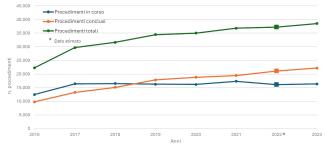
Data collection/transmission of regional reclamation procedures has been increasing since the first year of compilation of the indicator (2016) (Figure 1).
The general trend (2016-2023) highlights a significant increase for ongoing proceedings from 2016 to 2017 (+31.7%), and then stabilized with minimal fluctuations. After the peak of 2021, a decrease was recorded (-5.6%) in 2023. The completed proceedings, however, show a consistent growth, in particular between 2016 and 2017 (+35.4%). Even if the growth is less marked in the following years, a constant increase is still observed until 2023 (+14% compared to 2021) (Figure 1).
As regards total procedures, a more stable trend is observed compared to the other categories, with constant and progressive growth until 2023 (+4.7% compared to 2021) (Figure 1).
From the analysis of the annual data it emerges that 2017 marks the greatest increase for all categories, suggesting a significant improvement in the management of the compilation and verification of databases. The completed procedures have a continuously growing trend, physiological in the context of the management of reclamation procedures and in the way in which the registers are compiled. Similarly, a certain tendency towards stabilization of ongoing proceedings could suggest an improvement in the management of new cases.
Data
Figure 2: Number of sites subject to remediation procedures, ongoing and completed, and progress in the management of sites with ongoing procedures
ISPRA
-
Total sites with ongoing procedure
-
Total sites with completed procedure
-
Sites in the notification phase
-
Sites in the conceptual model phase
-
Sites in the intervention phase
Table 1: Sites subject to regional remediation procedures recorded in regional registries/databases
ISPRA processing based on data from SNPA, Regions and Autonomous Provinces
Update: 01/01/2024
Table 2: Surface area of sites subject to regional remediation procedures recorded in regional registries/databases
ISPRA processing based on data from SNPA, Regions, Autonomous Provinces
Update: 01/01/2024
Table 3: Progress in the management of sites with ongoing remediation procedures
ISPRA processing based on data from SNPA, Regions, Autonomous Provinces
Update: 01/01/2024
Table 4: Contamination status of sites subject to remediation procedures (ongoing and completed)
ISPRA processing based on data from SNPA, Regions, Autonomous Provinces
Update: 01/01/2024
Table 5: Sites with completed administrative remediation procedure, with or without intervention
ISPRA processing based on data from SNPA, Regions, Autonomous Provinces
Update: 01/01/2024
Table 6: New remediation procedures initiated in 2022 and 2023
ISPRA processing based on data from SNPA, Regions, Autonomous Provinces
Update: 01/01/2024


Information on the progress of site management with the remediation process is available for the entire national territory with the exception of the Sardinia region.
The number of sites registered in each regional registry/database does not remain constant but increases over time with the activation of new procedures; in fact, sites with completed proceedings continue to remain included in the registry/database. The total number of sites registered in the regional registers/databases is made up of ongoing and concluded proceedings. The sites with ongoing administrative proceedings registered so far are mainly located in Lombardy (21%), Campania (19%) and Tuscany (13%), similarly those with completed proceedings are mainly located in Lombardy (43%) and Tuscany (14%). Compared, however, to regional values, the highest percentages (above 70%) of sites with administrative proceedings concluded are found in the autonomous province of Bolzano (89%) and in Valle d'Aosta (83%), in Friuli-Venezia Giulia (83%), in Lombardy (74%) and in the autonomous province of Trento (76%). From the available data updated to 12/31/2023 it appears that 59% of the procedures are in the notification phase, 21% are in the conceptual model phase and 20% are in the intervention phase (Figure 2). The highest percentages found at regional level with reference to the most advanced state of the procedure, i. e. The so-called "sites in the intervention phase", are observed in Lombardy (28%), Piedmont (12%) and Tuscany (11%) (Table 3).
The administrative area affected by known reclamation procedures is equal to 45,474 hectares and relates to 56% of the procedures. The technical surface area is equal to 11,457 hectares and relates to 30% of the proceedings. For 62% of the procedures at least one surface area data (administrative or technical) was provided (Table 2). Examining the data of the ongoing proceedings, the administrative surface is equal to 25,461 hectares and is related to 57% of the ongoing proceedings, while the technical surface of the ongoing proceedings is known only in 21% of the cases. Of the completed procedures, the percentage of sites for which the administrative surface area is known is 56% and is equal to 20,013 hectares; the technical surface area, equal to 5,499 hectares, is known for 38% of the sites with completed proceedings.
The state of contamination is defined for 97% of sites with ongoing proceedings and for 98% of those with completed proceedings. Of the total sites subject to remediation procedures, ongoing and completed (38,556), 14.3% (5,502) are awaiting investigations, 16.6% (6,400) are potentially contaminated, 10.3% (3,974) are contaminated while 56.3% (21,721) are not contaminated (Table 4), for the remainder 2.5% (959) information on contamination status is not available.
The reclamation procedures were concluded without the need for intervention in 70% of cases and in 30% following intervention (Table 5).
The type of intervention adopted (reclamation, MISP, MISO, mixed intervention) in the sites with an approved intervention and in those with a completed intervention is represented respectively in Figures 3 and 4. Detailed information on the type of intervention is available for 74% of the sites with proceedings underway and in the intervention phase (2,601), from which it appears that in 77% of cases it is a reclamation intervention, in 12% MISP and in 6% MISO (Figure 3). In the case of sites with completed interventions (6,568), this detailed information is available for 61% of the sites which shows that in 88% of cases it concerns remediation and in 5% of MISP and in 1% of MISO (Figure 4).
In 2022, 1,288 procedures were activated. The Lombardy region records the maximum value with 678 procedures, while it should be noted that some regions have not recorded new activations.
In 2023 the total was slightly higher, with 1,305 proceedings activated (Table 6).